What has caused my Diaphragm to Fail? Comet MC & P36 Range
4 November 2019 | Admin
TWO CUTS AT THE SUCTION AND DISCHARGE VALVES
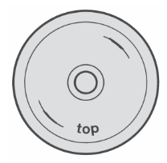
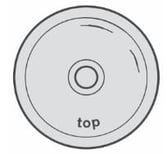
There are several causes to take into account for this type of problem: - As usual, the first thing to do is to check if the suction line is clogged and clean the filter.
- One of the most common causes is cavitation, vapor bubbles form inside the fluid which implode and ruin the diaphragm. To avoid cavitation there are several useful tips, first of all you should not suck water from excessive depths (maximum 4 meters).
- If the liquid is too thick, use a water-based liquid
- Excessive speed may also damage the diaphragms, it is good practice to keep below 550 RPM
- Always check that the suction valve is closed correctly and that the liner holes are positioned correctly.
- In addition, the diaphragm may also be affected by chemical aggression, always check the compatibility between the diaphragm and the chemical product used.
BREAKAGE CLOSE TO THE INNER DIAMETER AND LACERATIONS
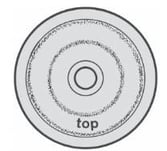 This is a breakage due to wear, when the diaphragm is used beyond the permitted time (300 hours) the retention disc causes a friction and then lacerations.
This is a breakage due to wear, when the diaphragm is used beyond the permitted time (300 hours) the retention disc causes a friction and then lacerations.
It is good practice to change the diaphragms every 300 hours or at the beginning of every season (the shorter of the two).
SEMI-CIRCULAR SHARP CUT
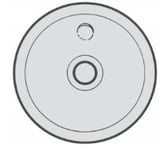 This cut is produced by the presence of air in the oil bath under the diaphragm. The air was probably not purged when assembling or repairing, and the diaphragm must now be replaced, taking care to purge the air from the pump.
This cut is produced by the presence of air in the oil bath under the diaphragm. The air was probably not purged when assembling or repairing, and the diaphragm must now be replaced, taking care to purge the air from the pump.
CIRCULAR CUT, CORRESPONDING TO THE PISTON DIAMETER IN THE LOWER PART OF THE DIAPHRAGM
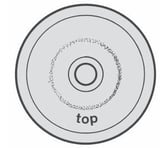
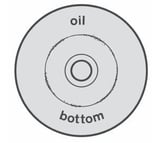
This damage can have several causes: - Lack of oil between piston and liner, to be filled up
- Excessive suction pressure, check that the pump is not supplied by a positive pressure water mains (if this is the case, disconnect)
- Pump speed too low, increase RPM according to the instruction manual
- Incorrect position of the liner holes
- Delivery valve open
STRONG LACERATION AT THE RETENTION DISC, SWELLING, DECREASED HARDNESS, INCREASED OUTER DIAMETER, INCREASED THICKNESS
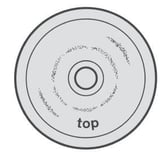
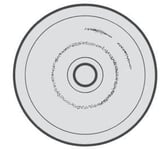
In this case the deformation is caused by chemical incompatibility between diaphragm and chemical product.


 This is a breakage due to wear, when the diaphragm is used beyond the permitted time (300 hours) the retention disc causes a friction and then lacerations.
This is a breakage due to wear, when the diaphragm is used beyond the permitted time (300 hours) the retention disc causes a friction and then lacerations. This cut is produced by the presence of air in the oil bath under the diaphragm. The air was probably not purged when assembling or repairing, and the diaphragm must now be replaced, taking care to purge the air from the pump.
This cut is produced by the presence of air in the oil bath under the diaphragm. The air was probably not purged when assembling or repairing, and the diaphragm must now be replaced, taking care to purge the air from the pump.


